Entering 2020, we anticipated that the pervasive secular innovation trends we have long focused our research efforts on, such as advanced computing, smart connectivity, digital resilience and the future of work, would continue to gain traction. However, we did not predict the accelerated pace at which this would occur over the course of the year. The digital transformation of humanity, across all demographics and geographies has been mandated by the measures implemented by governments and health organisations across the planet in order to tackle the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Long-Term Structural Themes Remain Intact
As we stated in the first instalment of our Disruptive Innovation series earlier in the year, “disruptive innovation accelerates during times of crisis…” Consequently, we have seen a swathe of strong evidence to suggest that the convergence of long-term secular growth themes is driving an even broader application of technology, which in turn provides an expansive set of opportunities for investors. For instance, the double disruption scenario created by technological innovation and a global health pandemic, has catalysed the digitalisation of global economies and a large-scale shift to remote working, learning and training. Accordingly, we have experienced a surge in operate-from-anywhere arrangements and increased awareness of the marketplace for the technologies that support this paradigm.
Similarly, as commerce increasingly moves online (see chart below), brick and mortar retailers are frantically rushing to transition stores in distribution facilities and social media platforms are establishing their roles as digital marketplaces, developing social commerce patterns that we have already seen emerge in China. In turn, this is driving demand for digital payment tools as small and medium-sized businesses, governments and consumers seek more efficient, economical and resilient methods of transaction and delivery of services. The ease of transacting online is broadening the spectrum of the digital transformation theme to areas such as education, health care and grocery commerce, which have moved from nascent to early stages of adoption during the pandemic.
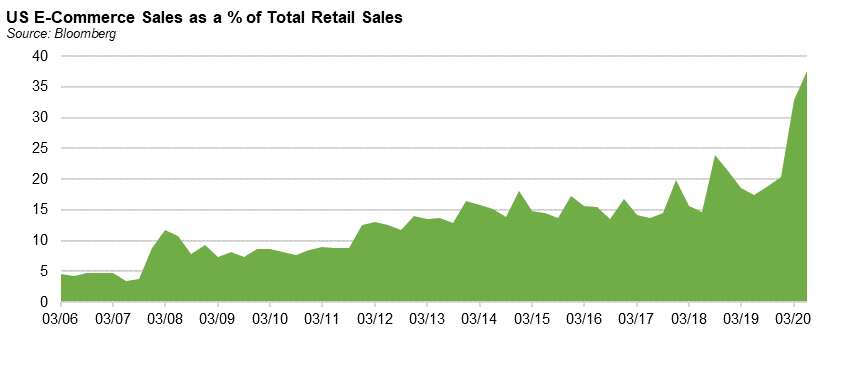
As a COVID-19 vaccine is rolled out globally, we believe that societies will gradually revert to ‘a new normal,’ whereby humankind becomes more reliant on technology to enhance the flexibility, convenience and sustainability of our everyday lives. In this environment, technology is (in our view) poised to gain a greater share of the global economy and we believe that those companies best-positioned to capture a material portion of this growth will be those firms that enable advanced computing platforms, smart connectivity, digital resilience and the “Future of Work.”
Valuation Considerations
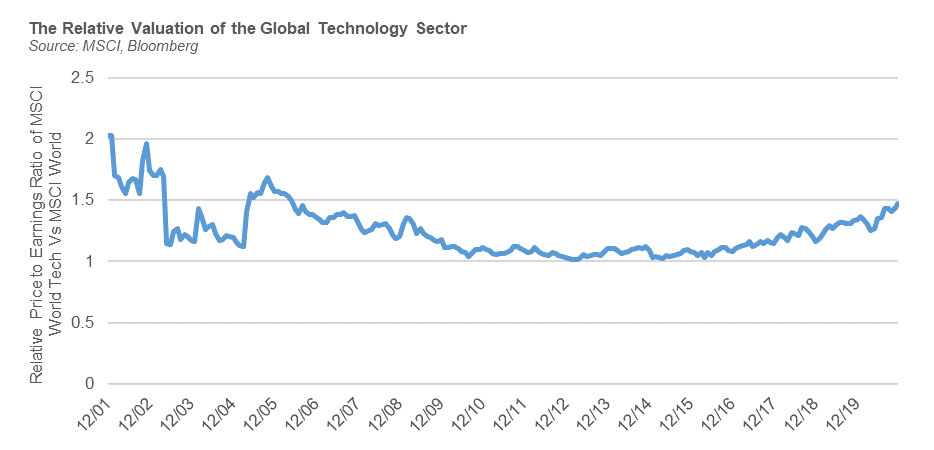
Unsurprisingly, we typically find a large number of disruptive innovators in the traditional Technology sectors, and our conviction for the growth prospects of this area of the market remain high. However, we recognise that a combination of ultra-accommodative monetary policy and COVID-19 conditions has driven a rapid acceleration in valuations in certain segments of the sector. As the chart below illustrates, the valuation (based on the market price of companies compared to their twelve month forward (consensus) estimated earnings) of the technology sector as a whole relative to the broader global equity market is elevated relative to recent trading patterms, but remains within historical ranges. We view this as reasonable and broadly attractive given the superior growth profile and balance sheets of many of the sector’s constituents, a dynamic we believe could continue in 2021.
Nevertheless, the bifurcation in valuations within the sector is extreme by historical standards and this partly reflects the increasing diversity within the Technology sector. It also, however, indicates that there are pockets of hype (with some companies trading on more than 30 times’ forecasted revenues), which in our view warrants caution and a disciplined valuation-aware approach.
We Remain Consistent in Our Strategy and Approach
We are living in through period of exceptional change that is characterised by the digitalisation of everything and the simultaneous transition to a low carbon economy. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted, and in many cases accelerated these structural shifts that (in our view) will continue long after crisis. We therefore see a strong positive correlation between sustainable development, innovation and long-term value creation and we believe that the Amity International Fund remains well positioned to benefit from the long-term secular trends catalysed by disruptive innovation. Our investment framework gravitates towards the identification of high quality companies that positively impact the planet and society, while at the same time ensuring that we remain on the right side of disruptive forces that impact business models, sectors and global economies more broadly. Additionally, we remain consistent in applying our valuation discipline and maintaining the highest standard of liquidity controls.
Glossary of Terms
Advanced Computing: Power computing platforms such as cloud services, artificial intelligence programmes and the associated silicon required to power these.
Smart Connectivity: We define it as a collection of connectivity solutions (including 5G, 4G, Mobile, IoT, next generation WiFi) that enable digital systems to match human actions in a natural fashion (i.e. high speed, low latency).
Digital Resilience: Advances in computing and connectivity bring obvious security concerns as well. The increasing proliferation of a large number of devices, combined with the increasing complexities of digital networks has substantially increased our vulnerability from a cybersecurity perspective, and thus cybersecurity is and needs to be a key focus of all industries seeking to achieve digital transformation in the future.
The Future of Work: Historically, work and education was location-centric, the devices used were mostly stationary (desktop and laptop), and most workflows focused on teams and cohorts that were in the same location. In the “Future of Work” era, education, training and employment becomes location agnostic, powered by always-on, always-available cloud-based software that is both intuitive and data-rich, and enables employees and students to be as productive on a smartphone or tablet as they are at a PC.